In this post we explain the fundamentals of M&A, we describe specialists who are part of the M&A process, and we highlight 12 most common jargons used during an M&A transaction.
What is M&A?
M&A stands for Mergers and Acquisitions. M&A is a process where companies sell and buy each other. There can be instances where even individuals invest or buy small businesses.
When an entrepreneur decides to sell his business, the reasons can be many. He may want to retire, relocate to a different city, focus on another business or simply move on from the business and receive a lucrative offer to buy a beach property.
|
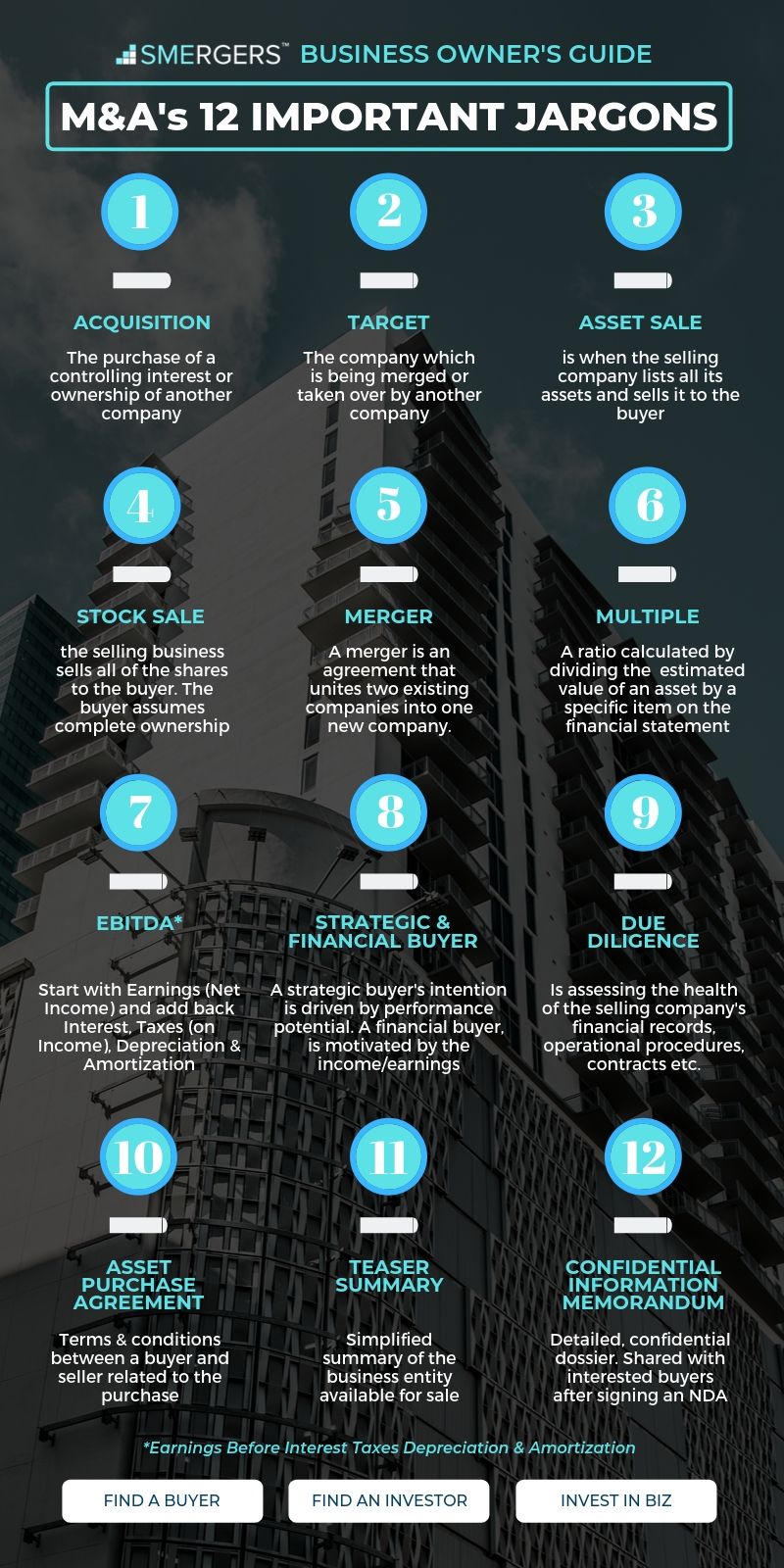
General terms jargons |
|
Types of sales: asset sales, stock sales and mergers
Regardless of the reason for a sale or a purchase of a company, there is a methodical process of transaction. There are three ways in which a company can gracefully sell its business.
- Asset sale
- Stock sale
- Merger
|
Types of sales jargons |
|
Essential Business Selling Guide: 12 Sure Shot Ways to Maximize your Business
Why do sellers sell a business?
As mentioned earlier, the reasons a company would present itself in the market for sale company can be many. While many a times it is related to personal reasons of the business owner – retirement, relocation, health, etc, it could also be due to business related reasons such as::
- The business has matured and has decent market penetration and is the right time to sell
- The company is unable to raise funds to scale
- The business has valuable patents and wants to capitalize on the current market value
- The business is in an industry where its competing with multinational giants and is ripe for a purchase
- The business becomes much harder to run, especially when competition is tough and competitors have deep pockets and can sustain losses for a long period of time
Why do buyers buy a business?
From a buyer's point of view, the decision to buy a business is simple. A buyer would be interested to acquire a company rather than building a product or service organically from scratch - which would take a lot of investment, time and effort.
Instead, buying a business which is doing well and has paying customers and vendor contracts to sustain business processes appears as a smarter option to jump start and focus on growth. Buyers may also want to acquire a business when:
- They want to cater to a new customer market where it is tough to break into the segment
- Kick-starting a new product or service line is required
- Speed of starting a product of service is critical
- To overcome barriers of entry in a tough market
- To eliminate the complexities of starting a competing product or service
In such cases, it is easier for the buying entity to buy their way into the product or business segment, as opposed to starting a new product division from scratch.
Examples of this would be when Facebook acquired WhatsApp. Facebook could have created its own mobile messaging app and spend a lot of money promoting it, but it found it wise to buy an established, popular platform which had already acquired millions of users. Another example is Tesla Motors acquiring Maxwell Batteries to enhance its battery platform through Maxwell's Supercapacitor technology, instead of relying on its current Lithium Ion battery platform.
Essential Business Buying Guide: 20 Questions you need to Ask Before Buying a Business
|
Selling, buying and valuation jargons |
|
Who's involved in the M&A process
Between the selling and the buying entities, there are individuals or firms who smoothen the process of performing due diligence, paperwork, business valuation and a whole host of tasks which need to be completed for a successful business sale.
To begin with, there are Business Brokers and Investment Bankers. Both tend to accomplish a common task - help sellers prepare for the sale and market their business to find the best buyer.
Business Brokers start with creating an initial business document called a Teaser Summary which contains simplified highlights and advantages of acquiring the selling company, and a Confidential Information Memorandum which is a detailed document about the business - this document contains confidential information, and will be shared with interested buyers once they sign an NDA (Non Disclosure Agreement).
Business Brokers are a lot like Real Estate agents. While Investment Bankers work on larger deals, Business Brokers and M&A advisors work on deals in the SME (small and medium enterprise) segment. Some of the tasks business brokers and investment bankers deal with are:
- Business valuation
- Deal discovery, advertising and match making
- Advisory services in structuring the sale of the business
- Assessing risks and liabilities in selling or buying
- Assisting in performing due diligence
- Assisting in drafting contracts and agreements
- Negotiating deals between seller and buyer
Accountants are an important part of selling and buying a company as well. They do all the heavy lifting about taxation liabilities, terms, and conditions. They advise the selling or buying entities with all the tax legalities before signing the dotted line to make the purchase.
M&A lawyers are vital as they run the entire deal. He or she is the lifeline of a merger or acquisition.
An M&A lawyer act as the primary point of contact and shepherds the transaction to a successful deal.
An M&A lawyer may be part of the business entity, but most likely they are hired for their expertise in practicing with an outside law firm. Some of their core competencies are as follows:
- Negotiation
- Multitasking
- Delegation
- Organization
- Complex drafting
- Attention to detail
An M&A lawyer is a legal jack of all trades.
Essential Tax Guide: Tax Implications of Selling a Business
|
M&A process jargons |
|
A single destination to find M&A advisors, brokers, bankers, investors, sellers, and buyers
The process of selling and buying a business is no small task, and it requires a specific set of skills at each state - preparing a business for sale, negotiating with a buyer, to conducting adequate due diligence and completing the share purchase. Advisors, lawyers, accountants and other consultants help make a successful business transaction.
We created SMERGERS to be a trustworthy network of entities who are willing to sell or buy companies and specialists who make the transactions possible. SMERGERS is a one stop destination for everything related to investing, buying, and selling businesses. Register on our website www.smergers.com to start building your network.




















